Embryo Freezing Procedure: A Complete Guide
Introduction
Embryo freezing, also known as embryo cryopreservation, is a technique used in assisted reproductive technology (ART) to preserve embryos for future use. The procedure involves the freezing and storage of embryos, which can be thawed and implanted in the uterus at a later date. Embryo freezing has revolutionized the field of infertility treatment, allowing patients to store embryos and increase their chances of achieving a successful pregnancy. In this article, we will explore the benefits, risks, process, success rates, and who can benefit from embryo freezing.
What are the benefits of Embryo Freezing?
Embryo freezing has numerous benefits, making it an increasingly popular option for couples struggling with infertility. One of the primary benefits of embryo freezing is the flexibility it offers in terms of timing. Embryos can be frozen at any stage in the IVF process, allowing for the postponement of pregnancy until the ideal time. This can be particularly useful for couples who want to focus on their careers or personal lives before starting a family.
Another benefit of embryo freezing is that it increases the chances of a successful pregnancy. Embryos that are frozen and thawed have been shown to have the same success rates as fresh embryos, meaning that there is a higher chance of a successful pregnancy with the use of frozen embryos. Additionally, embryo freezing allows for the preservation of excess embryos that are not used in the initial IVF cycle, providing couples with the option to have another child in the future.
Who Can Benefit from Embryo Freezing?

Embryo freezing can benefit a variety of people, including:
- Couples undergoing fertility treatment: Embryo freezing can be used in conjunction with IVF or ICSI procedures to increase the chances of a successful pregnancy. If the initial transfer fails, the frozen embryos can be thawed and transferred in subsequent cycles.
- Women facing cancer treatment: Chemotherapy or radiation therapy can damage the ovaries and affect a woman’s fertility. Embryo freezing can preserve her chances of conceiving after the treatment.
- Women who wish to delay childbirth: Women who wish to focus on their careers or have not found the right partner can freeze their embryos for future use.
What is the Embryo Freezing Process?

Here is a step-by-step guide to the embryo freezing process:
Step 1: Ovarian Stimulation and Egg Retrieval Before embryos can be frozen, they must first be created through in vitro fertilization (IVF). The IVF process starts with ovarian stimulation, which involves taking medications to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. Once the eggs are mature, they are retrieved from the ovaries using a transvaginal ultrasound-guided needle aspiration procedure.
Step 2: Fertilization After the eggs have been retrieved, they are fertilized with sperm in the laboratory. This can be done using conventional IVF or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), depending on the specific circumstances of the patient.
Step 3: Embryo Development Once the eggs have been fertilized, they are placed in a special incubator to allow them to develop into embryos. The embryos are carefully monitored over the next few days to ensure that they are growing and developing properly.
Step 4: Embryo Freezing On the third to fifth day after fertilization, the embryos are ready to be frozen. The embryos are carefully placed in a special solution that protects them during the freezing process. They are then placed in small, thin plastic straws and sealed at both ends.
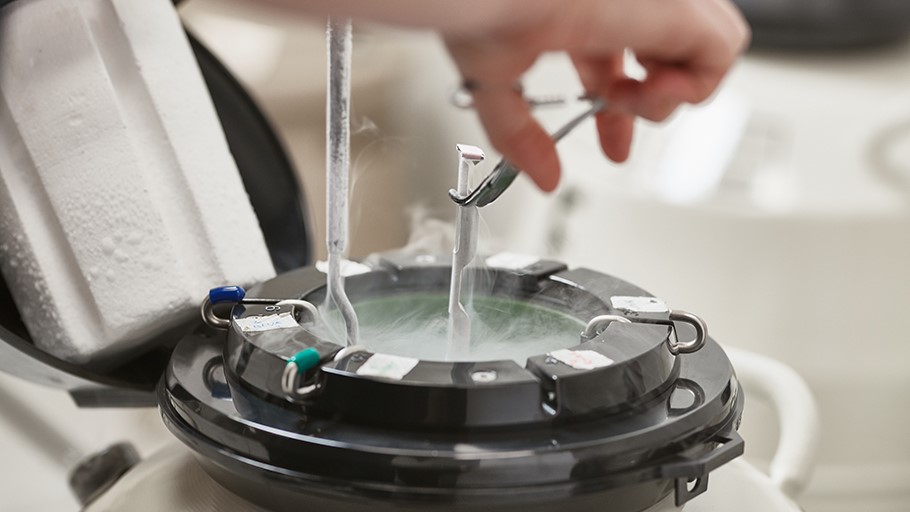
Step 5: Slow Freezing The straws containing the embryos are then placed in a controlled rate freezer, which gradually lowers the temperature to -196°C (-320.8°F). This slow freezing process helps to minimize damage to the embryos.
Step 6: Storage Once the embryos are frozen, they are transferred to liquid nitrogen tanks where they are stored at -196°C (-320.8°F) until they are needed. The embryos can be stored for many years, and the storage facility is carefully monitored to ensure that the temperature remains constant.
Step 7: Thawing and Transfer When the patient is ready to use the frozen embryos, they are thawed and prepared for transfer. This typically involves removing the embryos from the plastic straws and placing them in a special solution to help them adjust to their new environment. The embryos are then transferred to the uterus using a thin, flexible catheter.
What are the Success Rates of Embryo Freezing?

Success rates of embryo freezing can vary depending on a number of factors, including the age and health of the woman, the quality of the embryos, and the clinic performing the procedure. In this article, we will explore the success rates of embryo freezing and what factors can impact the success of the procedure.
Success Rates of Embryo Freezing: The success rates of embryo freezing have improved greatly over the years, thanks to advances in technology and technique. The American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) reports that the average success rate for pregnancy using frozen embryos is around 30-35% per transfer. However, success rates can vary greatly depending on several factors.
Age and Health of the Woman: The age and health of the woman are one of the most important factors in determining the success of embryo freezing. Women who are younger and in good health generally have higher success rates than older women or those with underlying health issues. This is because the quality of a woman’s eggs declines as she ages, which can lead to a lower success rate with embryo freezing.
Quality of Embryos: The quality of the embryos is another important factor in determining success rates. Embryos that are of good quality and have a high number of cells are more likely to result in a successful pregnancy than embryos that are of poor quality or have a low number of cells. Additionally, embryos that have been frozen for a shorter period tend to have higher success rates than those that have been frozen for a longer period.
Clinic Performing the Procedure: The clinic performing the embryo freezing procedure can also impact the success rates. Clinics with experienced and skilled embryologists tend to have higher success rates than those with less experienced staff. It’s important to do your research and choose a reputable clinic with a good track record of success.
A number of Embryos Transferred: The number of embryos transferred can also impact the success rates of embryo freezing. While transferring multiple embryos may increase the chances of pregnancy, it also increases the risk of multiple births, which can lead to complications for both the mother and the babies. The ASRM recommends transferring no more than two embryos for women under 35 and no more than three embryos for women over 40.
Wrapping it Up
Embryo freezing has become an increasingly popular option for couples who are struggling with infertility or who want to increase their chances of conception. While success rates can vary depending on several factors, including the age and health of the woman, the quality of the embryos, and the clinic performing the procedure, the average success rate for pregnancy using frozen embryos is around 30-35% per transfer. It’s important to work closely with a qualified fertility specialist and choose a reputable clinic with a good track record of success. If you are considering embryo freezing, contact Womb IVF to schedule a consultation with one of our experienced fertility specialists.